Irritable Bowel Syndrome by Artria Alexander RN BSN
Irritable bowel Syndrome (IBS)
is a common gastrointestinal disorder characterized by a cluster of signs and
symptoms that effects the process of digestion in the large intestine. The
process of food absorption and water absorption is compromised. IBS triad of
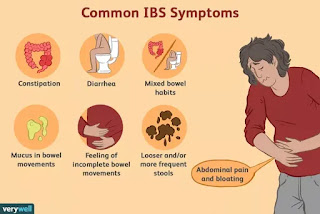
signs and symptoms include; cramping, abdominal pain, and altered bowel habits
(constipation/diarrhea).
Signs of IBS include abdominal distention, food
intolerance, and occasionally weight loss.
Factors that contribute to IBS are linked to muscle contractions in the intestine, abnormalities in the
nervous system including poor coordination between the brain and intestine,
inflammation of the large intestine, and severe infections caused by bacteria or
viruses. The symptoms of IBS can be triggered by food, stress and hormones.
Those who are at an increased risk of developing IBS include; females,
individuals under age 50, those with a family history of IBS, and those who have
preexisting mental health problems such as anxiety and depression.
To diagnosis and treat IBS, a comprehensive health history and physical exam are done. Diagnostic criteria include; X-ray, CT scan,
colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, lactose intolerance test, upper endoscopy, and
stool test. Treatment options are geared toward lifestyle and diet
modifications consisting of high fiber foods, the intake of plenty of fluids,
rest and adequate sleep, and exercise. Other options for treatment include
medication management such as fiber supplements (Metamucil), laxatives
(Miralax), anti-diarrheal medication (Imodium), anticholinergic medications,
(Bentyl), tricyclic antidepressants and pain medications (Neurontin).
Reference:
Chang, L.
(n.d.). Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). Retrieved November 23, 2019, from
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/irritable-bowel-syndrome.
Edited by Shirley Comer DNP, RN, JD, CNE, ACNS-BC, APN



No comments:
Post a Comment